GLOSSARY
Adolescence: The period of life starting with the appearance of secondary sex characteristics and ending with the ceasing of the body’s overall growth.
Central Precocious Puberty (CPP): A condition in which the physical and hormonal signs of puberty develop in children at an earlier age than is considered normal. CPP is caused by the early release of hormones by the brain.
Estrogen: Female sex hormone responsible for the development of secondary sex characteristics and involved in the reproductive cycle in women.
Follicle-stimulating hormone: A hormone released by the pituitary gland (a small gland at the base of the brain) that stimulates the ovaries to produce estrogen and the testicles to produce testosterone, which lead to the changes you see during puberty.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH): A hormone made by the hypothalamus (part of the brain) that causes the pituitary gland to release 2 other hormones: luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist: The most common treatment for CPP. GnRH agonists work by making sure the pituitary gland stops sending hormones to stimulate the ovaries and testes to produce sex hormones.
Hormone: A chemical substance produced in an organ of the body (like the adrenal glands or the pituitary gland) and carried to another organ or tissue in the body where it has a specific effect.
Luteinizing hormone: A hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates the ovaries to produce estrogen and the testicles to produce testosterone, which lead to the changes you see during puberty.
Pediatric endocrinologist: A doctor who specializes in the treatment of hormone-related conditions in children.
Pituitary gland: A small gland located at the base of the brain that helps control the release of hormones.
Precocious: Maturity that is unusually early for a person of that age; showing premature development.
Predicted adult height: An estimate of the height a child will reach based on the height of the child’s parents.
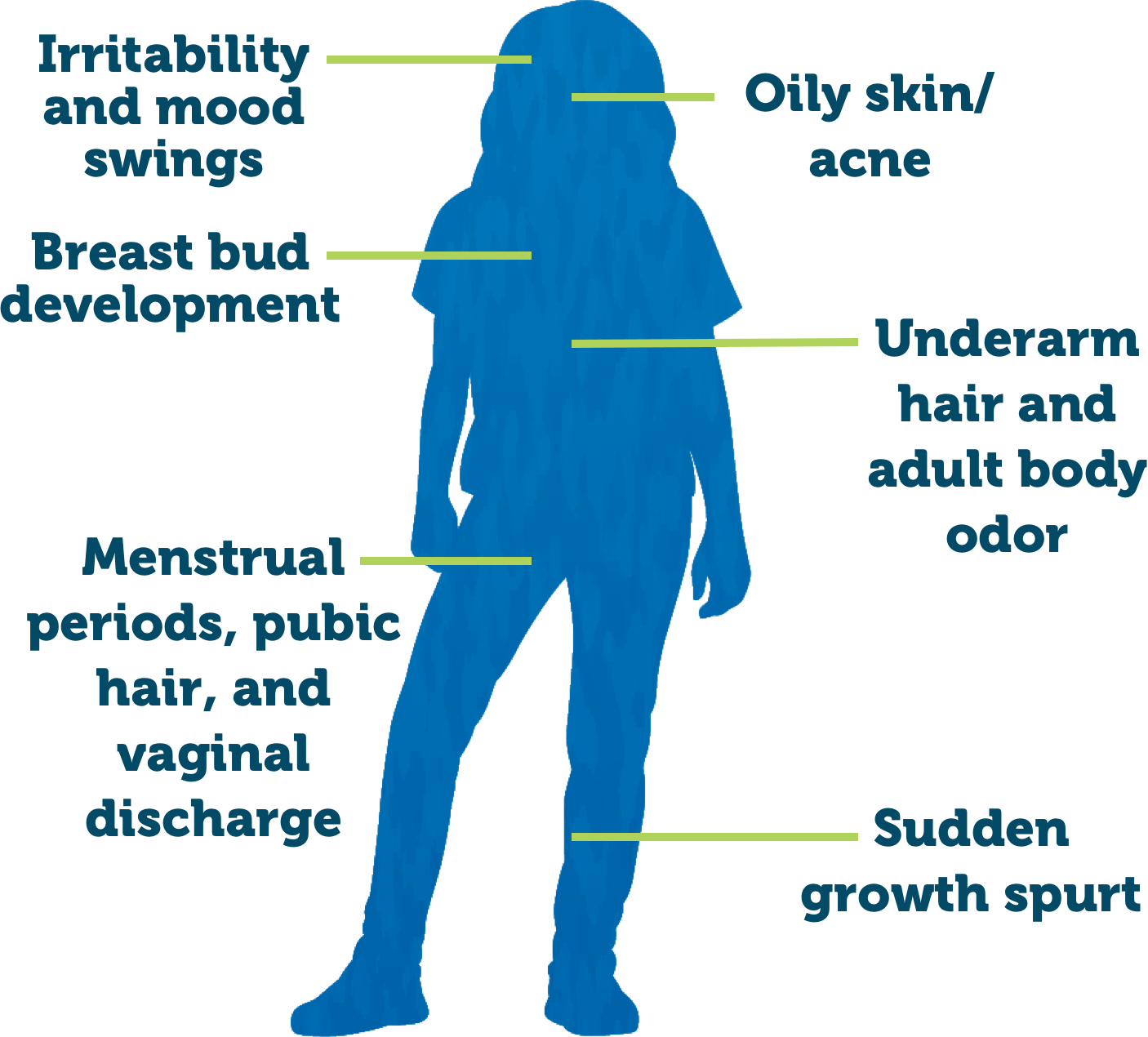
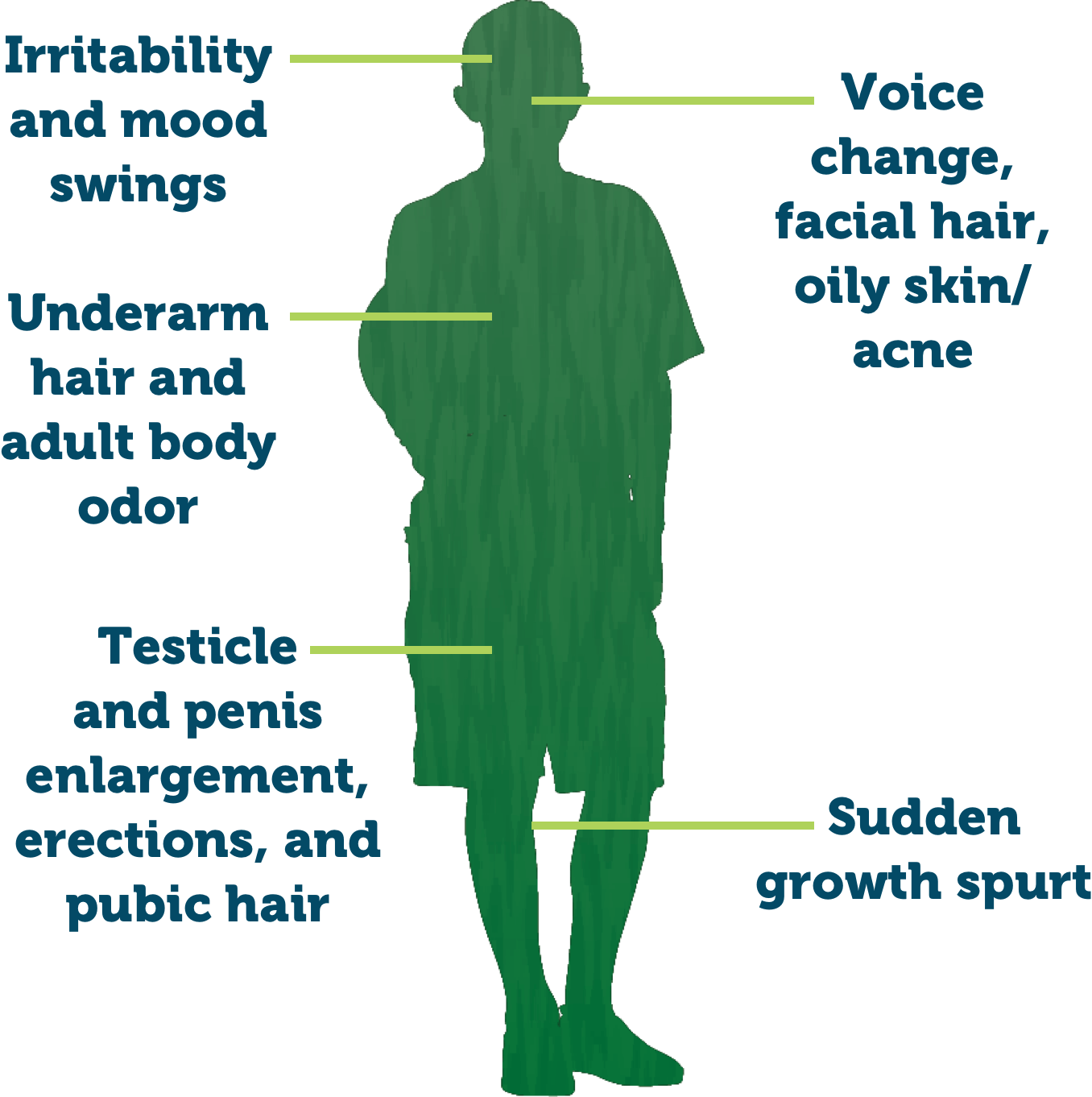
Puberty: The period when a person begins to develop secondary sex characteristics and becomes capable of sexual reproduction.
Reproductive hormone: A type of hormone involved in fertility and sexuality. Reproductive or sex hormones are usually made in the ovaries (in females) and testes (in males). In females, they include estrogen and progesterone. In males, reproductive hormones, such as testosterone, help develop and maintain male sex characteristics and help make sperm in the testes.
Suppression: To pause, reduce, or stop.
Testosterone: Male sex hormone (a small amount is produced by females as well) that is responsible for producing masculine secondary sex characteristics, such as growth of body hair and the development of the male reproductive system.